Data Packs - General Information
MineColonies allows modifications of many features using data packs, including player and worker recipes, loot tables, and mob drops. This allows broad expansion by players or modpack makers to support other mods, design choices, forms of progression, or styles of play. For general information on Minecraft data packs, see the official wiki.
Data packs exist as part of a world, and they must be installed on each world.
Concepts
Data packs are one or more files in the JSON format, stored within a folder or a zip file. Despite their names, these are text files, and can be opened with text editors. Note that Windows will, by default, hide the extension of known files, and this should be changed to avoid accidentally appending .txt to the file name. Avoid using a rich text editor like WordPad or Microsoft Word, which may insert additional formatting into the file. On Windows, simple text editors like Notepad, NotePad++, or WattPad are more useful for making small numbers of these files, and development environments like IntelliJ may be worth installing if creating many JSONs.
The JSON format is both generous and fastidious. It does not particularly care if you add extra fields, but it will choke on a missing comma or brace. Minecraft will report the file and location of a JSON error in the error log, but it may also be useful to check files in a JSON validator tool, colloqually known as a linter, as you create them. The JSON format will accept most characters, though the double-quotes (") and backslash (\) characters must first be 'escaped' by prefixing them with a backslash (such that " becomes \" and \\ becomes \\).
For most users, looking at other similar JSONs will be the fastest way to get started. For those interested in the specific rules of the format, see here.
The data pack folder or zip file can be any valid file name, and will be used to determine the name of the data pack. This folder or zip file must contain in its root level a file named pack.mcmeta, with a specific format. It is strongly encouraged to provide a distinct name and description for your data pack: this will show up as a tooltip from the in-game interfaces and /datapack list command. To act as a data pack, this should also contain a "data" directory.
Each folder within that data directory acts as a different namespace. Most mods have their own namespaces; for MineColonies, this is minecolonies. As a rule, all folders and files within a datapack, including the namespace folders, must have names consisting solely of lowercase alphanumeric characters, underscores (_), dashes (-), and/or dots (.). Any other characters, including uppercase letters, will cause Minecraft to fail to load the data pack, and give a largely unhelpful error. Completely empty names are considered legal and read, but not all mods will support them.
Data packs are very picky. A single misplaced comma, missing quotation mark, or invalid file name will give an error. If a file doesn't seem to be applying, or a datapack is giving errors on world load, check your file's formatting first. Files that exactly match the namespace, directory, and name of a file from vanilla Minecraft, a mod, or another data pack will either completely override or merge with that other JSON, depending on the file's type. A data pack can have multiple namespace directories, and the most common approach is to use a mod's namespace when directly overriding an existing JSON from vanilla or a mod, and a unique namespace when adding or modifying content or modifying another data pack. It's encouraged to add to the forge and minecraft namespaces only when adding to or modifying vanilla or forge defaults, to use the minecolonies namespace when modifying existing MineColonies files, and to use your own namespace when adding new types, or completely removing a crafter recipe or research.
Terminology
| Keyword | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Resource Location | The common word for Mojang's Namespaced IDs. A string of format namespace:path, with strict limitations on allowed characters, all lower-case, and only one colon (:). Used heavily in newer versions of Minecraft to uniquely identify nearly everything. |
| Namespace | The first half of a Resource Location, before the colon (:). In minecraft:cobblestone, "minecraft" is the namespace. Commonly used namespaces are "minecraft", "forge", and "minecolonies". Modpack makers may want to select their own namespace to avoid potential conflicts. In data packs, namespaces are derived from the names of the folders at the top level within the "data" directory. |
| Data Location | The internal location within namespaces that Minecraft and mods examine for specific uses, such as tags/blocks for Block Tags, or crafterrecipes for Crafter Recipes. Only JSONs within a known data location are applied by Minecraft or Minecraft mods, and Data Locations control how these JSONs apply and what format is expected. Relevant Data Locations are described in more detail throughout this document. |
| Path | The second half of a Resource Location, after the colon (:). In minecraft:cobblestone, "cobblestone" is the path. In data packs, Paths are derived from the folders and filenames within a specific Data Location. data/minecraft/tags/items/cobblestone.json will have a namespace of "minecraft", a Data Location of "tag/items", a path of "cobblestone". |
| Type | The supported format for a specific context. Includes Objects, Arrays, Strings, Booleans, Integers, and Doubles. |
| Object | In the context of the JSON standard, a group of key-value pairs held together by a pair of curly brackets ({ }). All JSON files must be a JSON Object, and name-value pairs may use an Object as a value. |
| Array | In the context of the JSON standard, a group of value types held together by a pair of square brackets([ ]). JSON Arrays may contain multiple Values, or multiple Objects, but not name-value pairs directly. |
| String | A set of characters. In JSON, strings must always be within quotation marks (" "). |
| Boolean | The values true or false, not contained within quotation marks. |
| Integer | A whole number. For this document, between positive and negative two billion, not contained within quotation marks. You generally won't use numbers that high. |
| Double | A number, including decimal numbers, not contained within quotation marks. |
| Name-Value Pair | In the context of the JSON standard, a string key and an matching value, usually in the format "name": value. Name-value pairs that are not the last name-value pair in an Object must be separated by a comma (,). |
| Name | In the context of the JSON standard, the left half of a name-value pair. Must be a String. Only one occurance of a name will be read in a single object's top level, usually the first, though sibling in an array or descendants in objects may hold the same Name. |
| Value | In the context of the JSON standard, the right half of a name-value pair. May be any type that matches the context. Values within quotation marks (" ") are treated as Strings. |
| Translation Key | A specially formatted string, which will attempt to be processed through the Minecraft translation file. If the client language file contains a matching Name, substitutes the corresponding Value, otherwise, presents the key to the user directly. |
Example Folder Layout
A complex data pack can have many files across many types in many namespaces, as shown below. Smaller data packs consisting of tweaks or settings changes may only have two or three files.
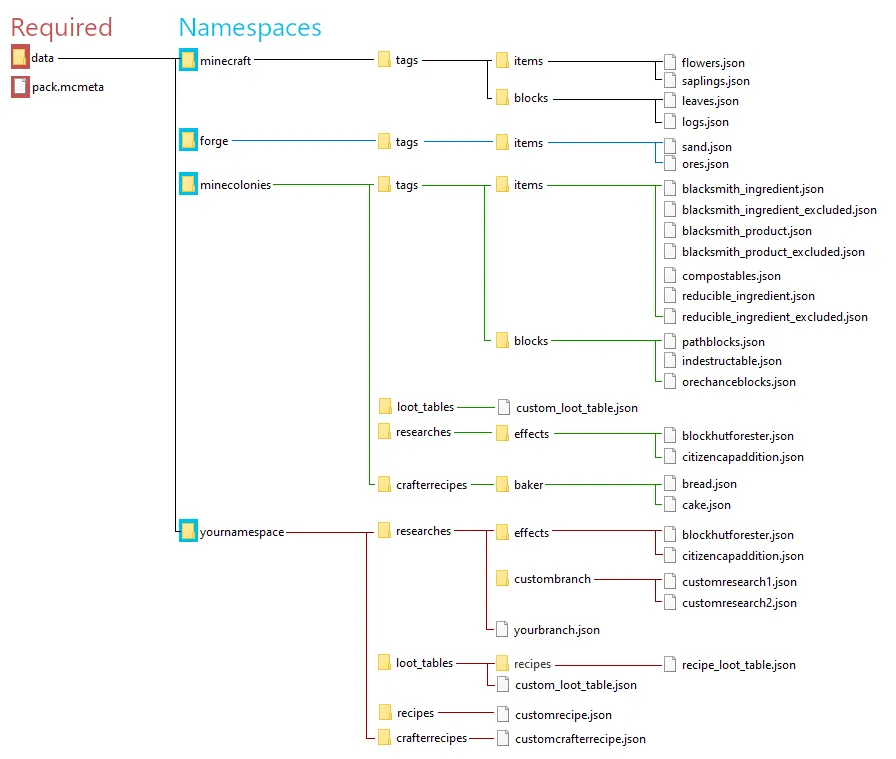
The pack.mcmeta file is mandatory, and Minecraft will not load a data pack without one, or with an improperly formatted one.
A typical pack.mcmeta file looks like this:
{
"pack": {
"pack_format": /* Any number, refer to https://minecraft.wiki/w/Pack_format for your Minecraft version */,
"description": "Rename To Your Preferences"
}
}
The "description"'s value is displayed to the user as an in-game title for the data pack, so it's best to make it descriptive and unique.
If changes are needed or you think there is content missing, feel free to edit this page or submit an issue for us to make edits. - MineColonies Wiki Team
